Installing a hydraulic flow control valve correctly is critical to system performance, yet over 70% of hydraulic failures trace back to improper installation or contamination introduced during setup. This guide walks through the complete installation process—from pre-installation safety checks to final calibration—using field-tested procedures and ISO standards that ensure reliable operation in industrial and mobile hydraulic systems.
Understanding Flow Control Valve Types and Mounting Configurations
Before starting any installation, you need to identify your valve type since each has specific mounting requirements and torque specifications.
Inline (Pipe-Mounted) ValvesInline valves connect directly into hydraulic tubing using threaded ports. These are common in mobile equipment and simpler systems where space isn't constrained. Port types include NPT/NPTF (Tapered Pipe Thread), SAE ORB (O-Ring Boss), and JIC 37° Flare.
Critical installation requirement: Inline valves must be mechanically supported with clamps or brackets. Never let the valve hang by connected hoses—vibration will fatigue fittings and cause failure.
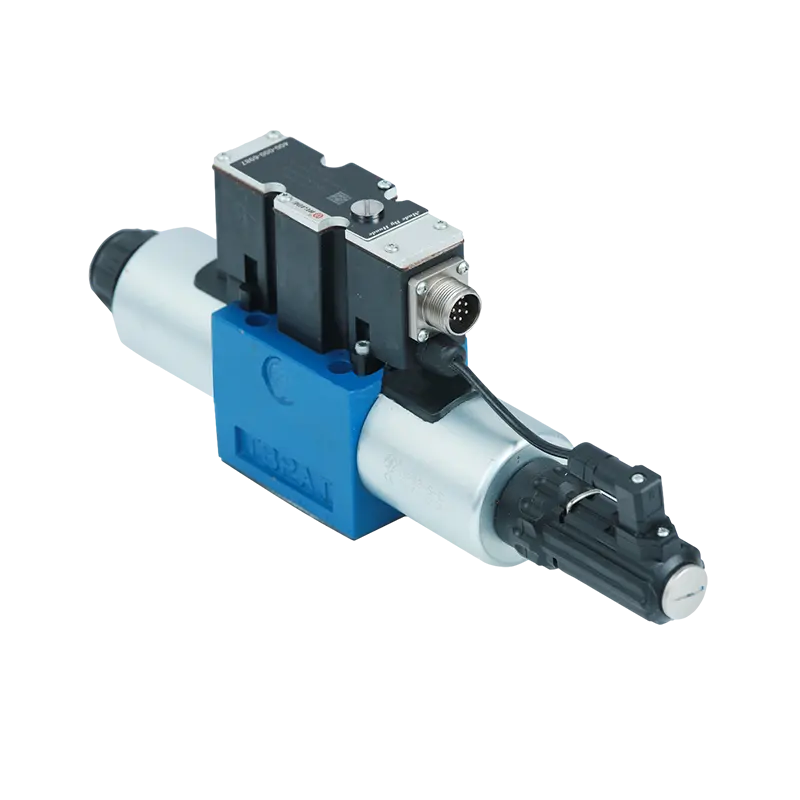
Subplate (Manifold) Mounted ValvesIndustrial systems use subplate valves where the valve body bolts to a precision-machined manifold surface. All flow paths are internal, eliminating external hose connections.
| ISO Size | NFPA Designation | Bolt Size | Torque Range (Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 4401-03 | D03 / NG6 | M5 | 5-9 |
| ISO 4401-05 | D05 / NG10 | M6 | 12-16 |
| ISO 4401-07 | D07 / NG16 | M10 | 63-70 |
| ISO 4401-08 | D08 / NG25 | M12 | 108-125 |
Sandwich (Stack) Valves: Install between a directional valve and subplate. Pay attention to orientation—many can be rotated 180° to change from meter-in to meter-out.
Cartridge (Screw-In) Valves: Thread directly into machined cavities. The challenge here is O-ring protection; cross-drilled passages can shear seals during installation if not properly lubricated.
Pre-Installation Safety and Preparation
Hydraulic systems store enormous energy even when shut down. Skipping energy isolation steps is the leading cause of installation injuries.
- Lockout/Tagout: Disconnect electric motors or engine ignition.
- Gravity Load Release: Lower all vertical loads (presses, cranes) to mechanical stops.
- Accumulator Discharge: Close isolation valves and slowly open manual bleed valves until pressure reads zero.
Particulate contamination causes more flow control valve failures than all other factors combined. Clearances are often 2-10 micrometers—smaller than a human hair.
| Component Type | ISO 4406 Code | Particles ≥4µm per 100ml |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Flow Control | 19/17/14 | 2500-5000 |
| Proportional Flow Valve | 18/16/13 | 1300-2500 |
| High-Precision Servo | 16/14/11 | 320-640 |
Step-by-Step Installation Procedures
Installing Inline Flow Control Valves- Verify flow direction: Look for the cast arrow. Installing a unidirectional throttle backward can cause dangerous uncontrolled motion.
- Fitting sequence: For SAE ORB, lubricate O-rings and torque to 25-35 Nm (-8 size). For JIC, ensure perfect alignment before tightening.
- Mechanical support: Install brackets within 150 mm of the valve body.
Inspect manifold surfaces for flatness (0.01 mm/100 mm) and roughness (Ra 0.8 µm). Tighten bolts in a star/cross pattern to 50% first, then 100% torque.
Circuit Configuration and Hydraulic Logic
How you connect the flow control valve determines system control characteristics, stiffness, and safety.
Meter-In ConfigurationFlow valve installed on the inlet side. Best for resistive loads (lifting, pushing). Critical limitation: Cannot control overrunning loads (gravity lowering), which causes runaway.
Meter-Out ConfigurationFlow valve installed on the outlet side. Creates a "hydraulic brake" by restricting return flow. Essential for overrunning loads.
In differential cylinders, meter-out creates pressure multiplication in the rod chamber. $$P_{rod} = \frac{P_{cap} \times A_{cap} + F_{load}}{A_{rod}}$$
Warning: Standard low-pressure return hoses may burst if not rated for this intensified pressure.
Diverts excess flow to tank. Highest efficiency but poor speed stiffness. Only suitable for constant loads like conveyors.
System Commissioning and Air Purging
Trapped air causes erratic motion (stick-slip) and cavitation noise.
- Set relief valve to minimum pressure (20-30 bar).
- Start pump at no-load.
- Open high-point bleed valves until fluid runs clear (milky fluid indicates air).
- Cycle actuators 5-10 times without load.
- Calibration: Perform final flow adjustments only when oil reaches operating temperature (40-60°C).
Common Installation Errors and Troubleshooting
Cavitation and AerationSymptoms include sharp crackling noise and vibration. Cavitation is caused by low pressure (check for high pressure drop or undersized lines); Aeration is caused by air entering suction lines (check pump seals and fittings).
Symptom: Actuator moves slowly when the valve is closed.
Reality: Spool-type flow control valves are not shutoff valves. They always have internal leakage (5-15 µm clearance). This is a design characteristic, not a defect.
Solution: Do not over-tighten the flow valve. Instead, install a pilot-operated check valve (counterbalance valve) downstream for zero-leakage load holding.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
| Interval | Inspection Item | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Visual inspection | Check for leaks; listen for cavitation |
| Monthly | Fluid analysis | ISO 4406 18/16/13 or better |
| Quarterly | Performance test | Measure cycle time (Acceptance: <10% variation) |
| Annually | Torque verification | Re-torque all manifold bolts and tie-rods |
When system performance meets specification from day one, you've eliminated the installation variables that cause 70% of field failures. Document your torque values and baseline performance—that's the difference professional installation technique makes.