This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about adjusting these important valves, using simple terms that anyone can understand.
What Is a Flow Control Valve?
A flow control valve is like a faucet for an industrial system. It controls how much fluid (which can be a liquid, a gas, or even a slushy mix called a slurry) moves through a pipe. By opening or closing a passage inside it, the valve can:
- Start or stop the flow completely.
- Speed up or slow down the flow.
- Direct the flow where it needs to go.
- Protect the system from too much pressure.
You'll find these valves in all sorts of places, from power plants and water treatment facilities to the heating and cooling systems in large buildings.
Common Types of Flow Control Valves
Not all valves are the same. Here are a few key types:
- Needle Valves: These are great for very precise, fine-tuned control, especially in smaller pipes.
- Globe Valves: Good for starting, stopping, and throttling (adjusting) the flow.
- Pressure-Compensated Valves: A smart type of valve that keeps the flow rate steady, even if the system's pressure changes. This is super important for machines that need consistent speed.
- On/Off Valves (Gate, Ball, Butterfly): These valves are designed to be either fully open or fully closed. They are not the best choice for precise flow adjustment.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Adjust a Flow Control Valve
Adjusting a valve changes the size of the opening that the fluid passes through. A smaller opening means less flow, and a larger opening means more flow. How you make that adjustment depends on whether the valve is manual, pneumatic (air-powered), or electric.
1. Adjusting Manual Valves
Manual valves are the simplest. You adjust them by hand using a wheel, knob, or screw.
For a Needle Valve:
- Find the adjustment screw.
- Turn it clockwise to make the opening smaller and reduce the flow.
- Turn it counter-clockwise to make the opening bigger and increase the flow.
- Make small turns (like 1/8 of a full circle) and watch how the system responds.
- Once you have it right, tighten the locknut so it doesn't change by accident.
For a Globe Valve:
- Use the handwheel to move the internal plug up or down.
- Turning it will position the plug somewhere between fully open and fully closed to get the flow rate you want.
2. Adjusting Pneumatic (Air-Powered) Valves
Pneumatic valves use compressed air to move. The adjustment often involves controlling the airflow to the valve's actuator (the part that physically moves it).
- Locate the adjustment screw on the actuator.
- Turn the screw counter-clockwise to let more air in, which makes the valve open or close faster.
- Some modern pneumatic valves have digital displays that make it easy to set and repeat the exact flow you need.
- Always lock the adjustment knob when you're done.
3. Adjusting Electric Valves
Electric valves use an electric motor (actuator) to make adjustments. These are often the most precise and can be controlled by a computer.
Simple Knob/Screw Adjustment:
Some electric valves have a simple knob you can turn clockwise to reduce flow and counter-clockwise to increase it.
Software-Based Adjustment:
- For high-tech systems, you connect a laptop to the valve's actuator.
- Using special software, you can tell the valve exactly how far to open or close.
- You can set limits, define what happens if it loses signal, and get very precise control. This is common in complex industrial settings.
Technical Note: How Valve Opening Affects Flow Rate
For engineers and technical buyers, it's helpful to understand the numbers behind the adjustment. The flow rate isn't just about how much you open the valve; it also depends on the pressure difference across the valve.
- Flow Units: Flow is typically measured in GPM (Gallons Per Minute) or L/min (Liters per Minute).
- The Cv Value: Every valve has a rating called a Flow Coefficient (Cv). This number tells you how many GPM of water will flow through the valve when it's fully open with a pressure drop of 1 PSI. A higher Cv means a higher flow capacity. The metric equivalent is the Kv value.
- Putting It Together: When you adjust a flow control valve, you are changing its effective Cv value at that position. To reach a target flow rate, you need to account for the system's pressure. For example, if you need a flow of 20 GPM in a system with a 50 PSI pressure drop, you would slowly turn the valve's handle and watch a flow meter until it hits your target. A small, gradual adjustment is always the best approach.
Safety First! Important Rules for Adjusting Valves
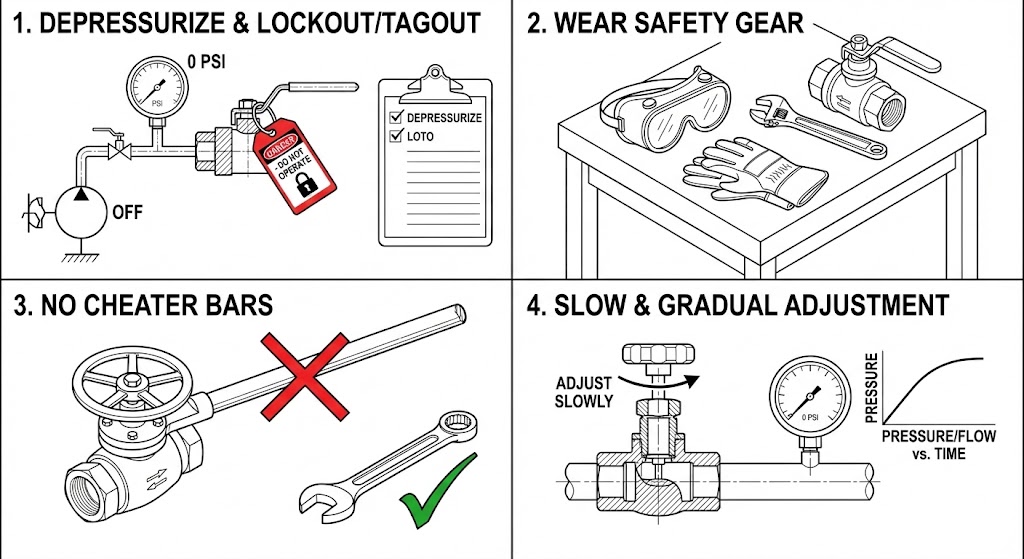
Working with industrial systems can be dangerous. Always follow these safety rules:
- NEVER adjust a valve while the system is under pressure. This is extremely dangerous and can cause serious injury.
- Always depressurize the system first. Follow your workplace's lockout/tagout procedures to make sure no one can turn it back on while you're working.
- Wear the right safety gear, like gloves and safety goggles.
- Don't use a wrench or cheater bar on a handwheel unless the manufacturer's instructions say it's okay. You could break the valve.
- Make adjustments slowly and gradually to avoid sudden changes that could damage the system.
Common Problems and How to Fix Them
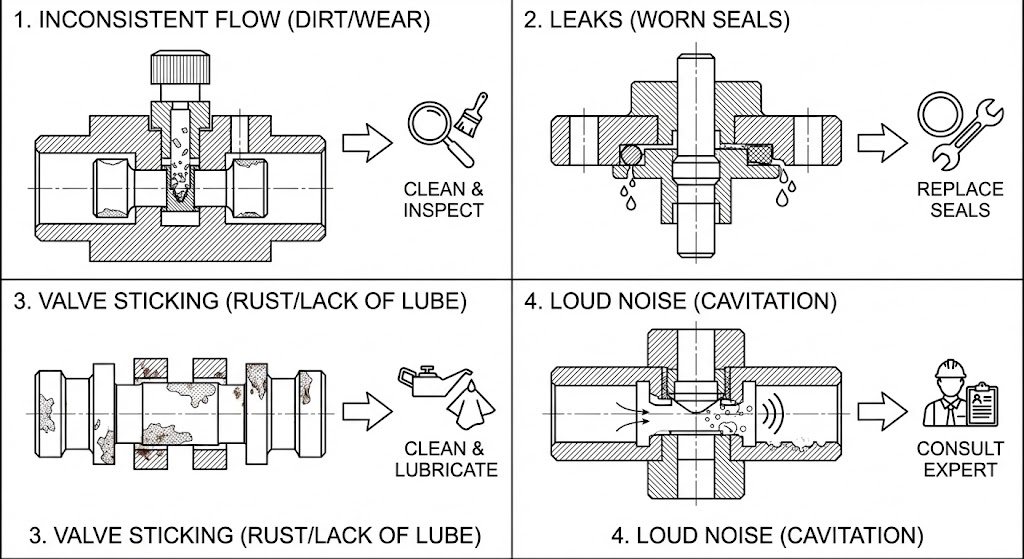
Even with perfect adjustment, things can go wrong. Here are some common issues:
- Inconsistent Flow: This could be caused by dirt in the valve, worn-out parts, or a bad adjustment. Fix: Clean the valve and check for worn parts.
- Leaks: Usually caused by old, worn-out seals. Fix: Replace the seals.
- Valve Sticking: Dirt, rust, or a lack of lubrication can cause the valve to get stuck. Fix: Clean and lubricate the valve.
- Loud Noise: This can be a sign of a serious problem like cavitation (when tiny bubbles collapse with great force), which can destroy the valve. Fix: This often means the valve is not the right size or type for the job. Consult an expert.
Why Proper Adjustment Matters
Taking the time to adjust a flow control valve correctly has huge benefits:
By understanding your system and following these steps, you can make sure your flow control valves are doing their job perfectly, keeping your operations safe and efficient.