In the world of fluid control systems, precision and reliability are paramount. Whether you're working in industrial automation, hydraulic systems, or pneumatic applications, the ability to control flow rates with exceptional accuracy can make the difference between optimal performance and system failure. This is where proportional flow valves come into play, serving as sophisticated control devices that have revolutionized how engineers approach fluid management.
Understanding the Basics
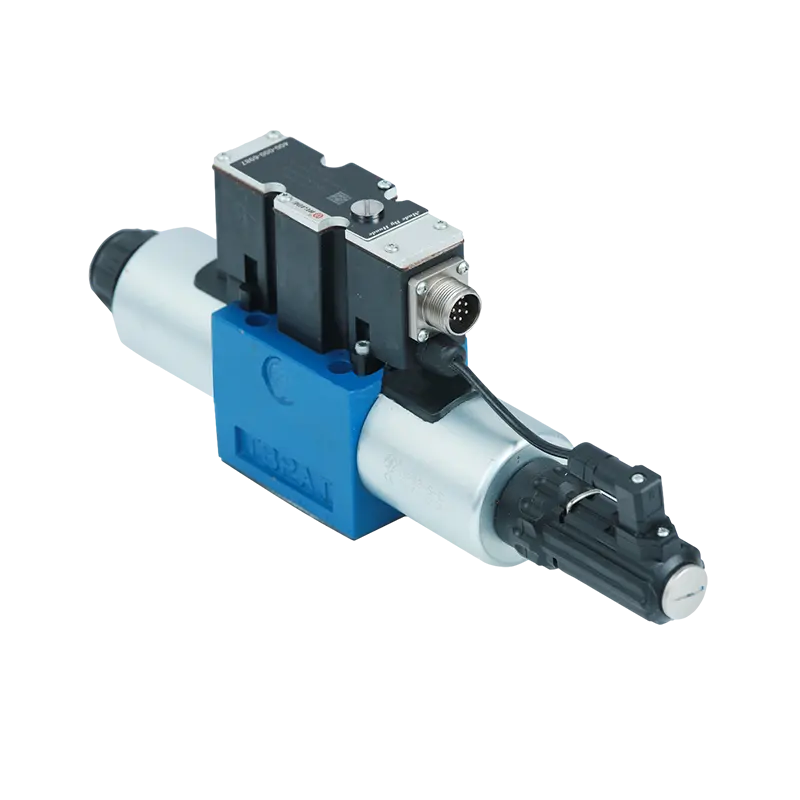
A proportional flow valve (art of the proportional valve family) is an advanced type of control valve that regulates fluid flow rate in direct proportion to an input signal, typically an electrical current or voltage. Unlike traditional on/off valves that simply open or close, proportional flow valves provide infinitely variable control within their operating range. This means they can maintain any desired flow rate between zero and their maximum capacity, responding dynamically to changing system demands.
The "proportional" aspect refers to the linear relationship between the input signal and the valve's opening position. For instance, if a valve receives a 50% input signal, it will open to 50% of its maximum capacity, delivering approximately 50% of its maximum flow rate. This predictable behavior makes these valves invaluable in applications requiring precise flow control.
How Proportional Flow Valves Work
The operation of a proportional flow valve centers around its electronic control system and mechanical actuator. The valve receives an analog input signal, commonly a 4-20 mA current loop or 0-10V voltage signal, from a control system such as a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or dedicated flow controller. [Understand how proportional valves work mechanically]
This electrical signal is processed by the valve's internal electronics, which convert it into mechanical motion through various actuator technologies. The most common actuators include proportional solenoids, servo motors, or voice coil actuators. These actuators precisely position the valve's flow control element—typically a spool, poppet, or needle—to achieve the desired flow opening.
Many modern proportional flow valves incorporate closed-loop feedback systems using position sensors or flow sensors. This feedback allows the valve to continuously monitor its actual position or the resulting flow rate and make real-time adjustments to maintain accuracy, even when system conditions change due to pressure variations or temperature fluctuations.
Types and Configurations
Proportional flow valves come in several configurations to suit different applications. Direct-acting valves control flow through a single port, making them ideal for simple flow regulation tasks. Pilot-operated valves use a small pilot stage to control a larger main stage, enabling high flow capacity while maintaining precise control sensitivity.
Two-way proportional flow valves control flow in a single direction and are commonly used for flow regulation applications. Three-way valves can direct flow between two outlets or combine flows from two inlets, making them suitable for diverting or mixing applications.
The internal design varies based on the application requirements. Spool-type valves offer excellent flow characteristics and are prevalent in hydraulic systems. Poppet-type valves provide tight shut-off capabilities and are often used in pneumatic applications. Needle valves excel in applications requiring very fine flow adjustment and are common in precision dosing systems.
Applications Across Industries
Proportional flow valves find applications across numerous industries where precise flow control is critical. In manufacturing and automation, they control the speed of hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic actuators, enabling smooth and precise motion control in assembly lines, packaging equipment, and material handling systems.
The automotive industry extensively uses these valves in testing equipment, paint spray systems, and hydraulic press operations. In aerospace, they're essential for fuel flow control, cabin pressurization systems, and hydraulic flight control actuators where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
Water treatment facilities employ proportional flow valves for chemical dosing, where precise amounts of treatment chemicals must be added to water streams. The pharmaceutical industry relies on these valves for precise ingredient dosing in drug manufacturing processes, where accuracy directly impacts product quality and regulatory compliance.
[See hydraulic proportional valve applications]
Advantages and Benefits
The primary advantage of proportional flow valves lies in their exceptional control precision. They can typically maintain flow accuracy within ±2-5% of the setpoint, far superior to manual valves or simple on/off controls. This precision translates into improved product quality, reduced waste, and better process efficiency.
Energy efficiency is another significant benefit. By providing only the exact flow needed at any given moment, proportional flow valves eliminate the energy waste associated with constant high-flow systems that use pressure relief valves or bypass circuits to manage excess flow.
The integration capabilities of these valves with modern control systems enable sophisticated automation strategies. They can respond to multiple input signals, participate in complex control algorithms, and provide diagnostic feedback to maintenance systems, supporting predictive maintenance strategies.
Selection Considerations
When selecting a proportional flow valve, several factors must be considered. Flow range is fundamental—the valve must handle both the minimum and maximum flow requirements of the application. Pressure ratings must exceed the maximum system pressure, including any pressure spikes.
Response time is critical in dynamic applications. Some systems require rapid flow changes, while others prioritize stability over speed. The control signal compatibility must match the available control system outputs, and the power requirements must align with available electrical supply.
Environmental conditions such as temperature extremes, vibration, and contamination levels influence valve selection. Media compatibility ensures the valve materials can handle the specific fluid without degradation or contamination.
Conclusion
Proportional flow valves represent a cornerstone technology in modern fluid control systems, offering the precision and flexibility required in today's demanding applications. Their ability to provide accurate, repeatable flow control while integrating seamlessly with electronic control systems makes them indispensable across industries ranging from manufacturing to aerospace.
As automation continues to advance and precision requirements become increasingly stringent, proportional flow valves will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in enabling efficient, reliable, and precise fluid control systems. For engineers and system designers, understanding these valves' capabilities and proper application is essential for developing optimized fluid control solutions that meet both current needs and future challenges.