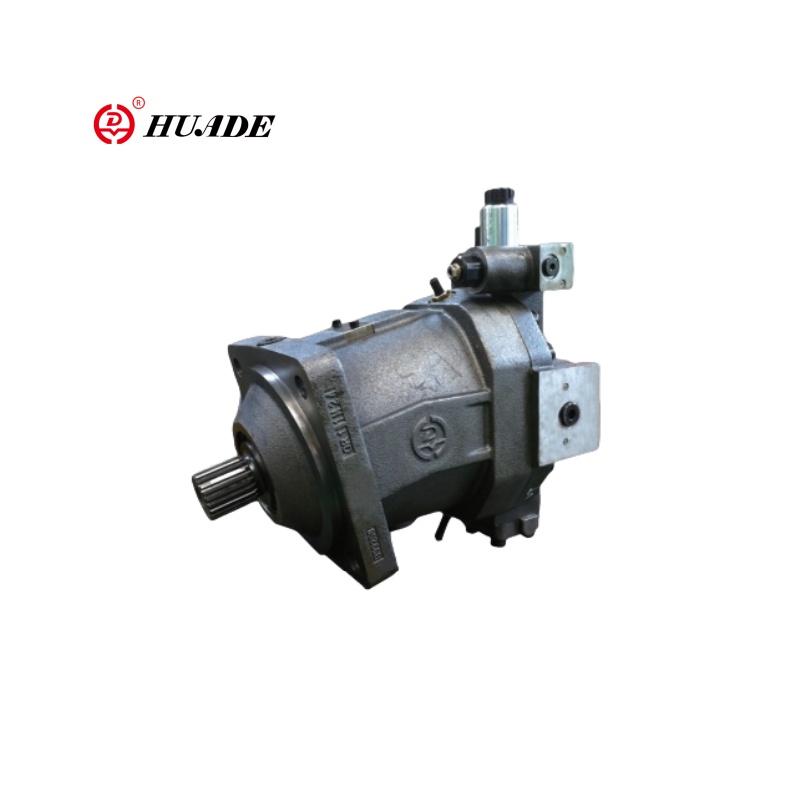
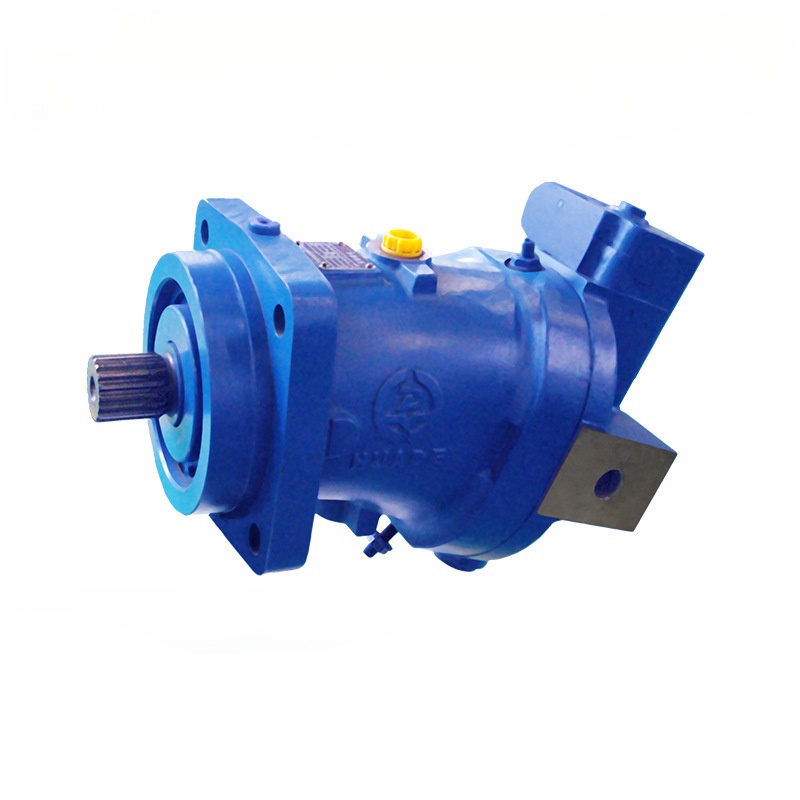
Have you ever wondered how heavy construction equipment like excavators can lift tons of weight with such precision? The secret often lies in a powerful device called an axial piston pump. These amazing machines convert the spinning motion of an engine into high-pressure fluid flow that can power everything from bulldozers to airplane landing gear.
In this guide, we'll break down exactly how axial piston pumps work, why they're so important, and where you'll find them in action. Don't worry – we'll explain everything in simple terms that anyone can understand.
What Is an Axial Piston Pump?
An axial piston pump is a special type of hydraulic pump that creates high-pressure fluid flow. Think of it like a powerful water gun that never runs out of water – it takes mechanical energy (like from an engine) and turns it into pressurized liquid that can do heavy work.
The word "axial" means the pistons inside move back and forth along the same direction as the main shaft. "Piston" refers to the moving parts that create the pumping action, just like pistons in a car engine.
These pumps are incredibly important because they can:
- Create very high pressure (up to 415 bar – that's like having 415 times the pressure of normal air)
- Work efficiently (up to 92% efficient)
- Control flow precisely
- Fit into tight spaces
The Basic Working Principle
The process of an axial piston pump begins with a simple concept: changing the size of chambers to move fluid. Here's how it works in easy steps. [Understanding whether axial piston pumps create pressure is key to grasping their power]
- The Rotation Begins: A motor or engine spins the main drive shaft of the pump. This shaft is connected to a cylinder block that holds several pistons (usually 7 to 11 pistons arranged in a circle).
- Pistons Start Moving: As the cylinder block spins, the pistons don't just go around in a circle – they also move back and forth (this is the "axial" part). This happens because of a special angled plate called a swashplate.
- Creating Suction and Pressure: When a piston pulls back, it creates more space in its chamber. This low pressure sucks fluid in from the inlet (like drinking through a straw). When the piston pushes forward, it squeezes the fluid out through the outlet at high pressure.
- Continuous Flow: Since multiple pistons are working at different times, there's always fluid being pumped out. This creates a steady, powerful flow of pressurized fluid.
Two Main Types
Axial piston pumps come in two main varieties, each with its own way of making pistons move.
[Learn about different types of piston pumps]
Swashplate Design
This is the most common type. Picture a coin lying flat on a table – now tilt it at an angle. That's essentially what a swashplate looks like. As the pistons spin around, they slide against this tilted plate, which forces them to move back and forth.
Key features:
- Very compact and lightweight
- Easy to adjust the flow by changing the swashplate angle
- Perfect for mobile equipment like excavators
- Smooth operation with less vibration
Bent-Axis Design
In this design, instead of having a tilted plate, the entire cylinder block is angled compared to the drive shaft. Imagine holding a flashlight at an angle – the cylinder block tilts the same way.
Key features:
- Extremely strong and durable
- Great for very high-pressure applications
- Handles both high pressure and high vacuum well
- Takes up more space but offers superior performance
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Swashplate Design | Bent-Axis Design |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Compact | Larger |
| Pressure Handling | High | Very High |
| Best For | Mobile equipment | Heavy-duty industrial |
| Adjustability | Very easy | Good |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
Inside the Pump
Let's take a look inside an axial piston pump to understand what makes it work:
Drive Shaft
This is like the pump's backbone. It connects to your motor or engine and transfers the spinning power into the pump. Without this, nothing would move.
Cylinder Block
Think of this as a carousel that holds all the pistons. It spins with the drive shaft and keeps all the pistons in perfect alignment as they do their work.
Pistons
These are the workhorses of the pump. Usually made from super-strong materials, they slide back and forth thousands of times per minute to create the pumping action.
Swashplate
This is the clever part that converts spinning motion into back-and-forth motion. By changing the angle of this component, you can control how much fluid the pump produces.
Valve Plate
This flat disk has special kidney-shaped holes that direct fluid flow. It ensures fluid enters when pistons are pulling back and exits when pistons are pushing forward.
Slipper Pads
These small but crucial parts connect the pistons to the swashplate. They're designed to slide smoothly even under enormous pressure.
Smart Controls
One of the coolest things about axial piston pumps is how controllable they are:
Speed Control
Want more flow? Spin the pump faster. Need less? Slow it down. The output flow is directly related to how fast the drive shaft spins.
Variable Displacement
Here's where it gets really smart. By changing the angle of the swashplate (or the tilt in bent-axis pumps), you can adjust how far the pistons travel. More angle = more fluid per revolution. Less angle = less fluid per revolution.
This is like having a car with an infinitely variable transmission – you can get exactly the performance you need for any situation.
Pressure Compensation
Some advanced pumps can automatically adjust themselves based on the system pressure. If the pressure gets too high, the pump automatically reduces its output to protect the system and save energy. It's like having cruise control for hydraulic systems.
Where You'll Find These Pumps in Action
Axial piston pumps are everywhere in our modern world, though you might not notice them:
Construction Equipment
Aerospace Industry
Marine Applications
Industrial Manufacturing
Why These Applications Choose Axial Piston Pumps
- High pressure capability: Can handle demanding tasks
- Precise control: Critical for safety and quality
- Compact size: Fits in tight spaces
- Reliability: Works consistently in tough conditions
- Efficiency: Saves fuel and energy costs
Comparing Pump Types: Why Choose Axial Piston?
Let's see how axial piston pumps stack up against other common types:
| Feature | Axial Piston | Gear Pump | Radial Piston |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Pressure | Very High (415 bar) | Medium (250 bar) | High (350 bar) |
| Efficiency | Excellent (up to 92%) | Good (85%) | Very Good (90%) |
| Size | Compact | Very Compact | Large |
| Flow Control | Precise & Variable | Fixed | Limited |
| Cost | Higher Initial | Low | Medium |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Low | High |
| Best Use | High-performance systems | Simple, cost-effective | Specialized high-pressure |
When to Choose Axial Piston Pumps
Choose an axial piston pump when you need:
- High pressure and high efficiency
- Variable flow control
- Compact design
- Long-term reliability
- Precise operation
Choose other pumps when you need:
- Simple, low-cost solutions (gear pumps)
- Ultra-high pressure with limited flow (radial piston)
- Maximum simplicity and low maintenance (gear pumps)
Maintenance and Reliability Tips
To keep your axial piston pump running smoothly:
Regular Maintenance
- Check hydraulic fluid regularly for contamination
- Inspect seals for wear or damage
- Monitor pressure to ensure proper operation
- Clean filters to maintain fluid quality
Warning Signs
Watch out for these problems:
- Unusual noise: May indicate bearing wear
- Reduced flow: Could mean internal wear
- Overheating: Might suggest efficiency problems
- Fluid leaks: Usually means seal replacement needed
Maximizing Lifespan
- Use clean, proper hydraulic fluid
- Don't exceed recommended pressure limits
- Keep operating temperatures moderate
- Follow manufacturer service schedules
Advanced Features for Professionals
Modern axial piston pumps include sophisticated features:
Electronic Controls
- Load sensing: Automatically adjusts output based on demand
- Pressure limiting: Protects system components
- Flow sharing: Distributes flow between multiple functions
- Diagnostic monitoring: Provides real-time performance data
Energy Efficiency
- Variable displacement: Reduces energy waste
- Pressure compensation: Optimizes power consumption
- Smart controls: Match output to actual needs
- Recovery systems: Capture and reuse energy
The Future of Axial Piston Pumps
Technology continues to improve these already impressive machines:
Current Trends
- Electro-hydraulic integration: Combining electric and hydraulic power
- IoT connectivity: Remote monitoring and control
- Advanced materials: Longer-lasting components
- AI optimization: Self-adjusting performance
Environmental Benefits
- Higher efficiency: Less fuel consumption
- Longer lifespan: Reduced waste
- Better control: Precise operation reduces energy waste
- Cleaner fluids: Biodegradable hydraulic oils
Conclusion: Why Axial Piston Pumps Matter
Axial piston pumps are truly remarkable machines that convert simple rotational motion into powerful, controllable hydraulic energy. Their combination of high pressure, precise control, compact size, and excellent efficiency makes them essential for countless applications in our modern world.
Whether you're operating heavy construction equipment, flying in an airplane, or using products made by precision manufacturing, you're probably benefiting from the work of axial piston pumps.
Key Takeaways
- Simple principle: Convert rotation to back-and-forth motion for pumping
- Two main types: Swashplate (compact) and bent-axis (heavy-duty)
- Smart controls: Variable displacement and pressure compensation
- Wide applications: Construction, aerospace, marine, and industrial
- Superior performance: High pressure, efficiency, and precision
- Future-ready: Continuously improving with new technology
Want to Learn More?
- Watch manufacturer videos and animations online
- Visit trade shows to see pumps in action
- Read technical guides from leading companies
- Consider hands-on training if you work with hydraulic systems
Understanding how axial piston pumps work gives you insight into one of the most important technologies powering our modern industrial world. From the excavator building your neighborhood to the airplane taking you on vacation, these remarkable machines are quietly doing the heavy lifting that makes modern life possible.