Have you ever wondered how massive construction equipment like excavators and bulldozers get their incredible power? The secret lies in a fascinating device called a hydraulic axial piston motor. Don't worry if that sounds complicated – by the end of this guide, you'll understand exactly how these amazing machines work!
What Is a Hydraulic Axial Piston Motor?
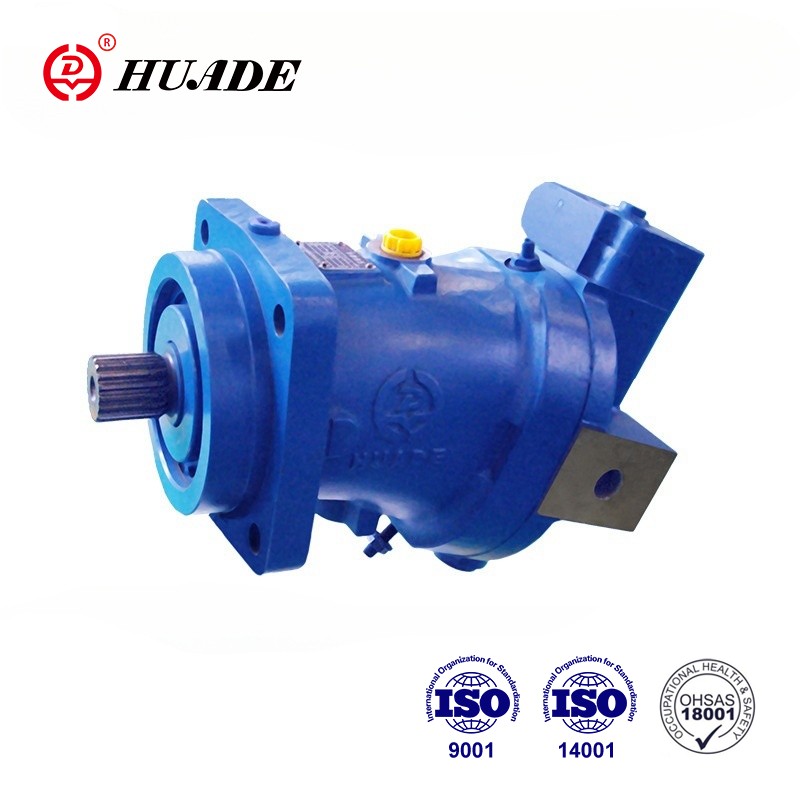
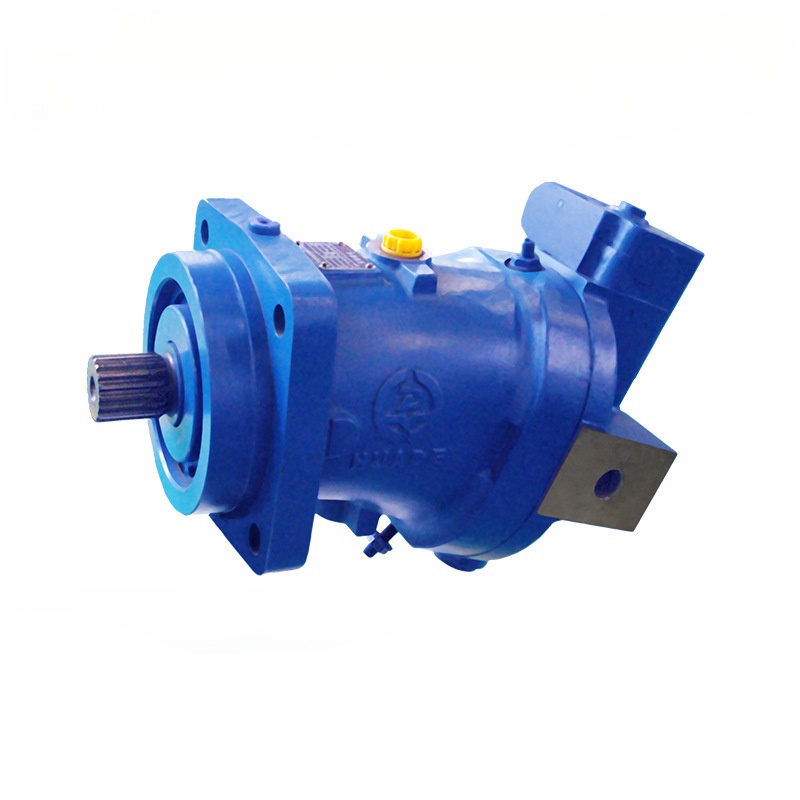
Think of a hydraulic axial piston motor as a translator. It takes the power from pressurized oil (hydraulic energy) and converts it into spinning motion (mechanical energy) that can move heavy things.
Simple Analogy: Imagine squeezing a water balloon – the pressure you create is similar to hydraulic pressure. Now imagine that pressure could spin a wheel to lift heavy objects. That's basically what a hydraulic axial piston motor does, but much more efficiently and powerfully.
Why Are These Motors So Important?
These motors are like the muscles of heavy machinery. They're used in:
The Magic Behind the Machine: How It Works
The Simple Version
Here's the basic idea in four easy steps:
- High-pressure oil enters the motor through special ports
- Pistons get pushed by this pressurized oil
- Linear motion becomes rotation through a clever tilted plate system
- The spinning shaft delivers power to move heavy equipment
The Detailed Process
Let's dive deeper into what happens inside:
Step 1: Pressure Input
High-pressure hydraulic fluid (usually special oil) flows into the motor through a component called a valve plate. This plate has kidney-shaped openings that control exactly when and where the fluid goes.
Step 2: Piston Power
Inside the motor, there are several pistons (usually 5, 7, or 9) arranged in a circular pattern within something called a cylinder block. When the pressurized fluid hits these pistons, it pushes them outward with tremendous force.
Step 3: The Conversion Trick
Here's where the magic happens! The pistons don't just move straight out – they're connected to either:
- A tilted plate (called a swashplate), or
- A bent shaft system (called a bent-axis design)
As the pistons move in and out, this tilted connection forces the entire cylinder block to rotate, just like pedaling a bicycle converts your leg motion into wheel rotation.
Step 4: Power Delivery
The rotating cylinder block is connected to an output shaft that spins and delivers power to whatever needs to be moved – tracks on an excavator, wheels on a loader, or arms on a crane.
Key Parts and What They Do
Let's break down the main components:
Essential Components
| Part | What It Does | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the pistons and rotates | Like the engine block in a car |
| Pistons | Convert pressure into motion | The "muscles" of the motor |
| Swashplate/Bent-Axis | Changes linear motion to rotation | The "transmission" system |
| Valve Plate | Controls fluid flow timing | Like traffic lights for oil flow |
| Drive Shaft | Delivers power to the load | The final power output |
| Piston Shoes | Reduce friction | Keep everything running smoothly |
| Seals & Bearings | Prevent leaks and support rotation | Maintain efficiency and durability |
How These Parts Work Together
The valve plate directs oil to pistons at precise timing. Pressurized pistons push against the tilted plate, forcing the cylinder block to rotate. Seals and bearings ensure smooth operation without energy loss.
Two Main Design Types
There are two popular ways to build these motors:
Swashplate Design
How it works: Pistons line up parallel to the main shaft and slide against a tilted plate
Best for: Precise control applications, compact spaces
Think of it as: A bicycle wheel where the spokes (pistons) push against a tilted surface
Used in: Injection molding machines, factory automation
Bent-Axis Design
How it works: The whole piston assembly is angled compared to the output shaft
Best for: Heavy-duty applications needing lots of torque
Think of it as: A bent elbow joint that converts motion
Used in: Mining equipment, construction machinery
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Swashplate | Bent-Axis |
|---|---|---|
| Size | More compact | Larger |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Torque | Good | Excellent |
| Speed | Excellent | Good |
| Best Use | Precision work | Heavy lifting |
Performance: What Makes These Motors Special
Why They're So Powerful
Hydraulic axial piston motors are like the athletes of the motor world. Here's what makes them special:
- High Efficiency: They convert 85-95% of hydraulic energy into useful mechanical work. That's like getting 95 cents of value for every dollar you spend!
- Incredible Torque: They can generate massive twisting force, even at low speeds. Imagine being able to slowly but powerfully turn a giant bolt.
- Precise Control: You can adjust their speed and power very accurately, like having a dimmer switch for incredible strength.
- Durability: With proper care, they can work 8,000-12,000 hours – that's like running non-stop for over a year!
The Numbers That Matter
- Efficiency: 85-95% (much better than other motor types)
- Pressure: Can handle 350-450 bar (that's about 5,000-6,500 pounds per square inch!)
- Speed Range: 100-3,000 rotations per minute
- Lifespan: 8,000-12,000 operating hours
Real-World Applications
Construction Sites
When you see an excavator digging or a bulldozer pushing earth, hydraulic axial piston motors are doing the heavy lifting. They provide the precise control needed to operate the bucket, tracks, and other moving parts.
Factories
In manufacturing plants, these motors run injection molding machines that make plastic parts, operate heavy presses, and power assembly line equipment.
Mines
Giant mining trucks and drilling equipment rely on these motors to handle the extreme conditions and massive loads found in mining operations.
Farms
Modern tractors and harvesters use these motors to power implements, drive wheels, and operate hydraulic systems that make farming more efficient.
Common Problems and How to Fix Them
Even the best machines can have issues. Here are the most common problems and their solutions:
| Problem | Symptoms | Common Causes | Quick Fixes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Rotation | Slow/weak turning | Low pressure, insufficient flow, internal leaks | Check pump pressure, verify flow rates, inspect seals |
| Oil Leaks | Visible oil puddles | Worn seals, loose fittings, cracked housing | Replace seals, tighten connections, inspect housing |
| Jerky Movement | Stuttering at low speeds | Dirty oil, worn parts, air in system | Change filters, bleed air, inspect components |
| Noise/Vibration | Unusual sounds, shaking | Loose mounting, worn parts, pressure spikes | Tighten bolts, check alignment, adjust pressure |
Maintenance Made Simple
Regular maintenance prevents costly breakdowns:
The Future of Hydraulic Motors
Technology improvements include smart monitoring sensors, advanced materials for longer life, quieter operation with less environmental impact, and computer-controlled precision adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
A: Hydraulic motors excel in high-torque, low-speed applications and can handle overloads better. Electric motors are better for high-speed, constant-load applications and are more energy-efficient overall.
A: Yes! Many hydraulic axial piston motors can reverse their operation to become pumps. This is useful in systems that need to both generate and use hydraulic power.
A: Choose swashplate for compact installations and precise control. Choose bent-axis for heavy-duty applications requiring maximum torque and durability.
A: These motors have very tight tolerances (gaps smaller than a human hair). Dirty oil causes wear that reduces efficiency and shortens motor life dramatically.
A: Prices range from $1,000 for small units to $50,000+ for large, high-performance motors. The investment pays off through their efficiency and long life.
Conclusion: Power in Motion
Hydraulic axial piston motors are remarkable machines that convert the simple concept of fluid pressure into incredible mechanical power. Whether you're operating construction equipment, running factory machinery, or maintaining agricultural equipment, understanding how these motors work helps you use them more effectively and keep them running longer.
The next time you see a massive excavator effortlessly lifting tons of earth or a factory machine precisely shaping metal parts, you'll know the secret behind their power – the hydraulic axial piston motor working its magic inside.
Remember, like any powerful tool, these motors perform best when properly maintained and operated within their design limits. With the right care, they'll provide years of reliable, efficient service, proving that sometimes the best technology is the result of brilliantly simple engineering principles applied with precision and care.
Want to learn more about hydraulic systems? Check out our related guides on hydraulic pumps, system design, and maintenance best practices. Understanding the complete hydraulic system helps you get the most from these incredible machines.