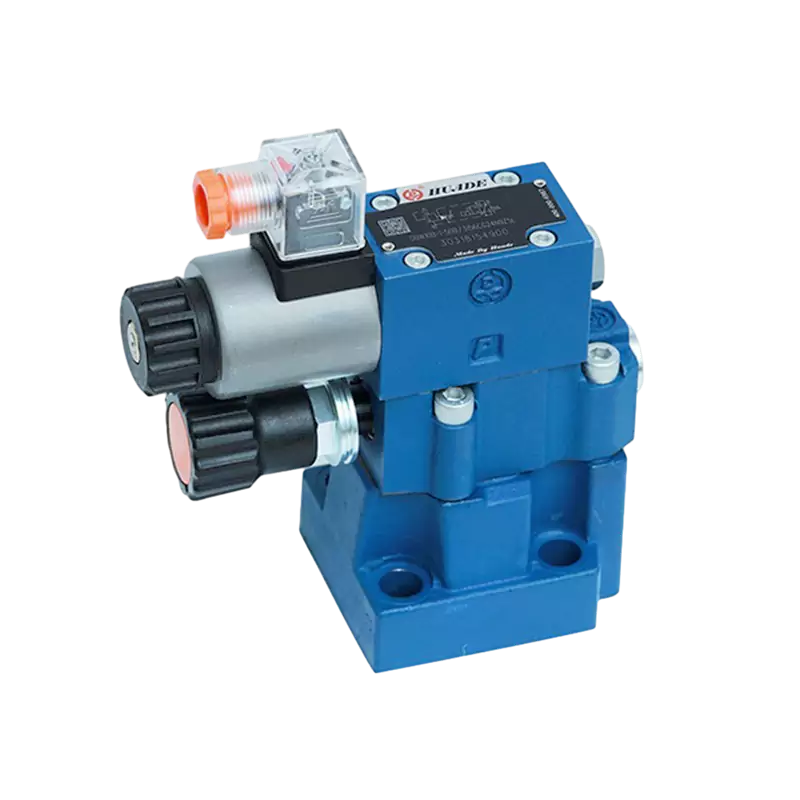
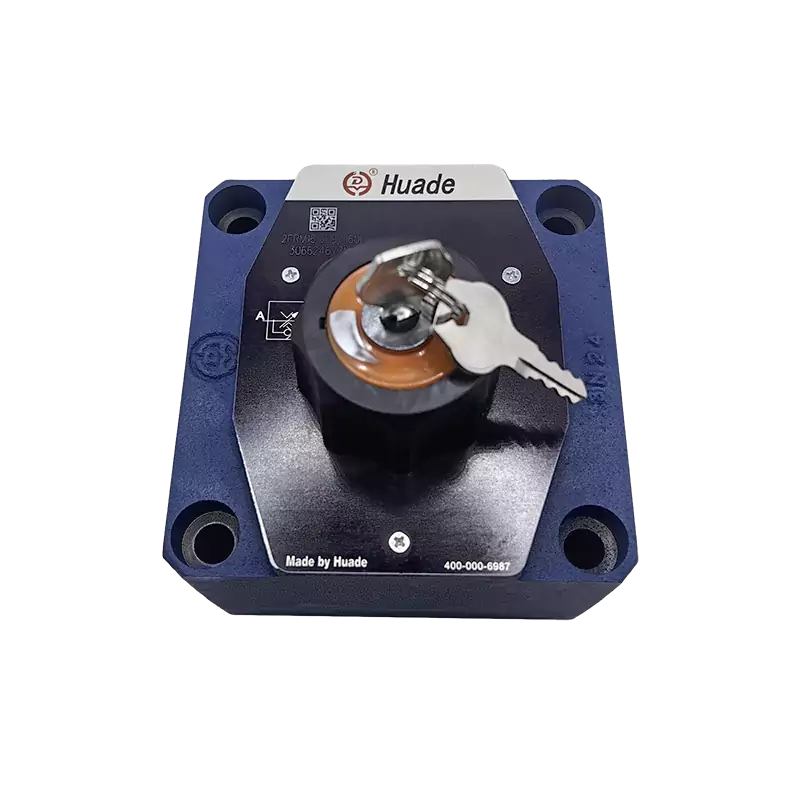
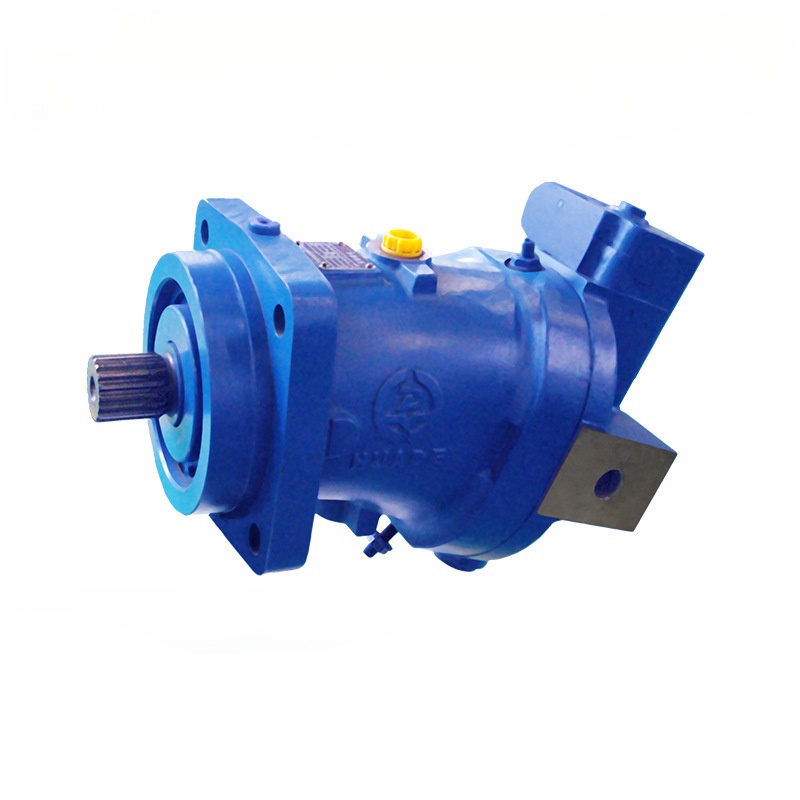
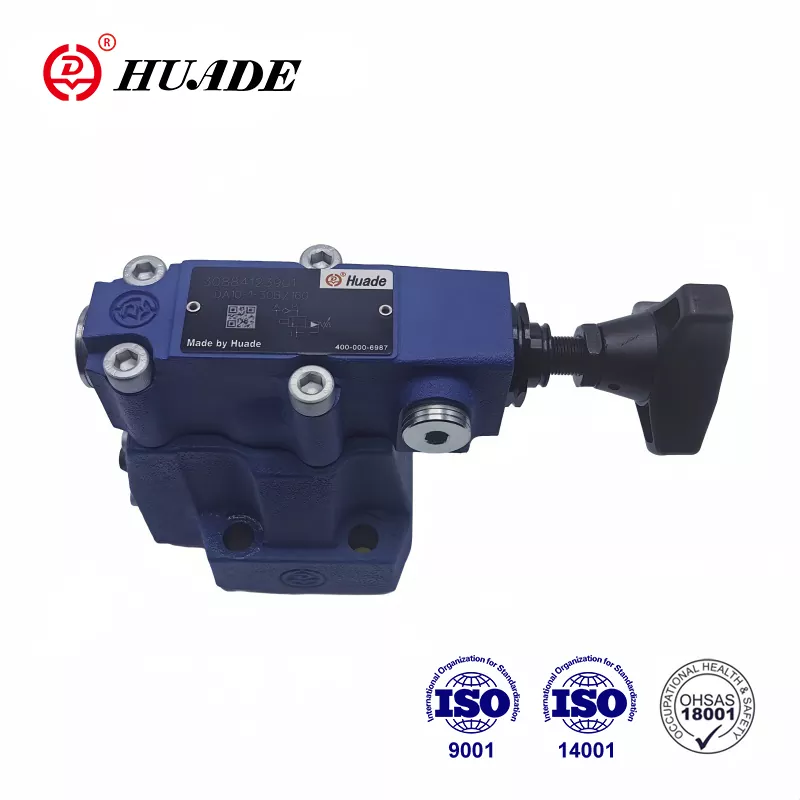
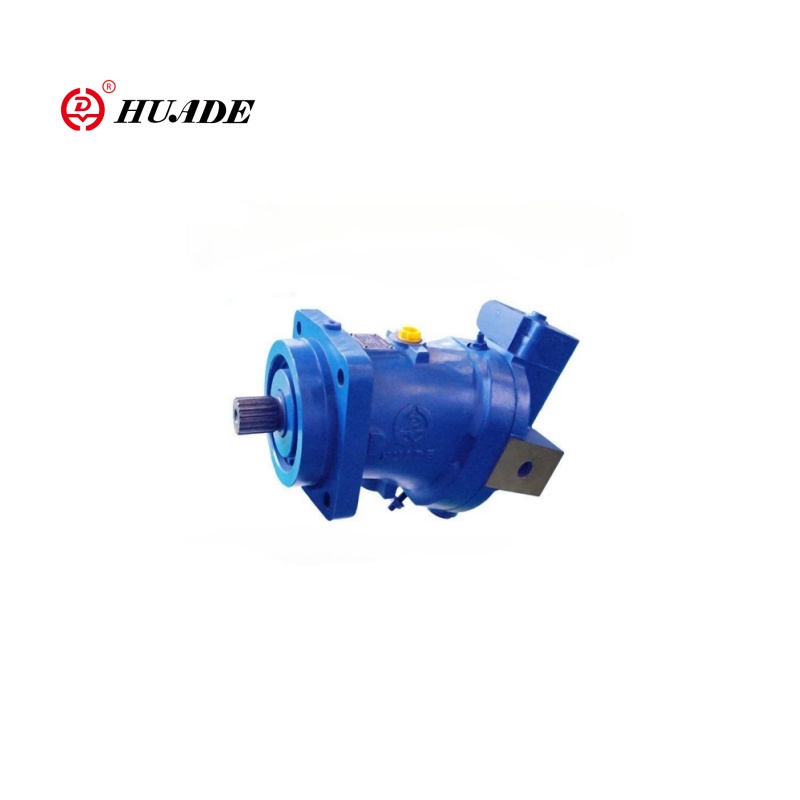
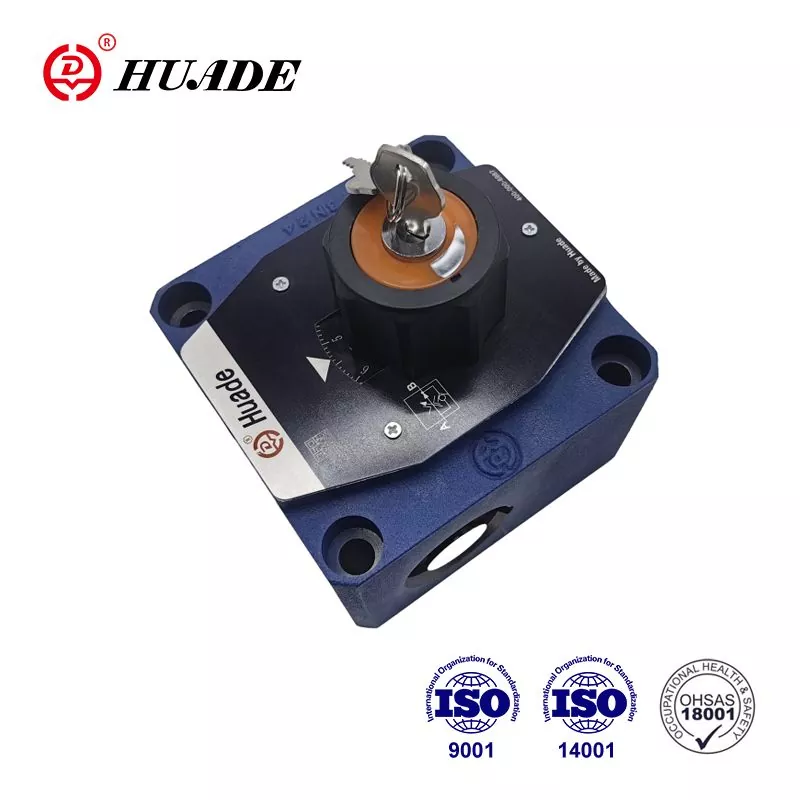
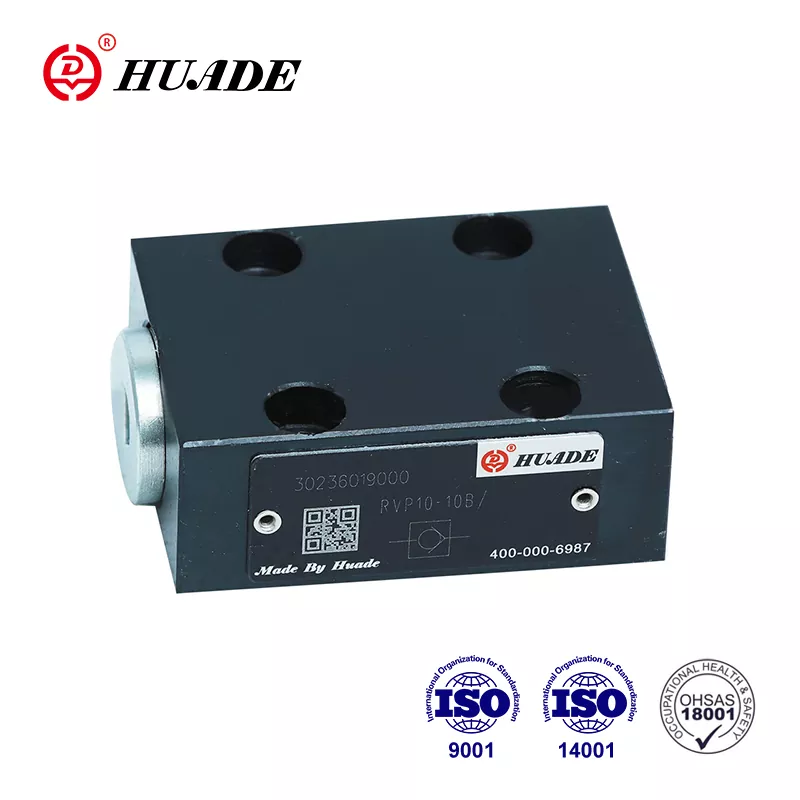
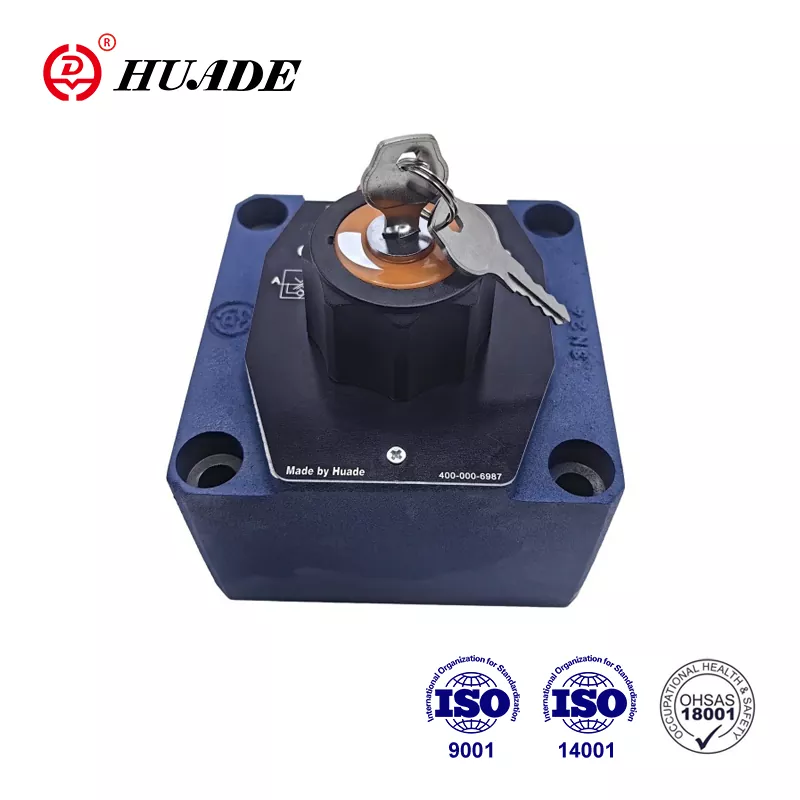
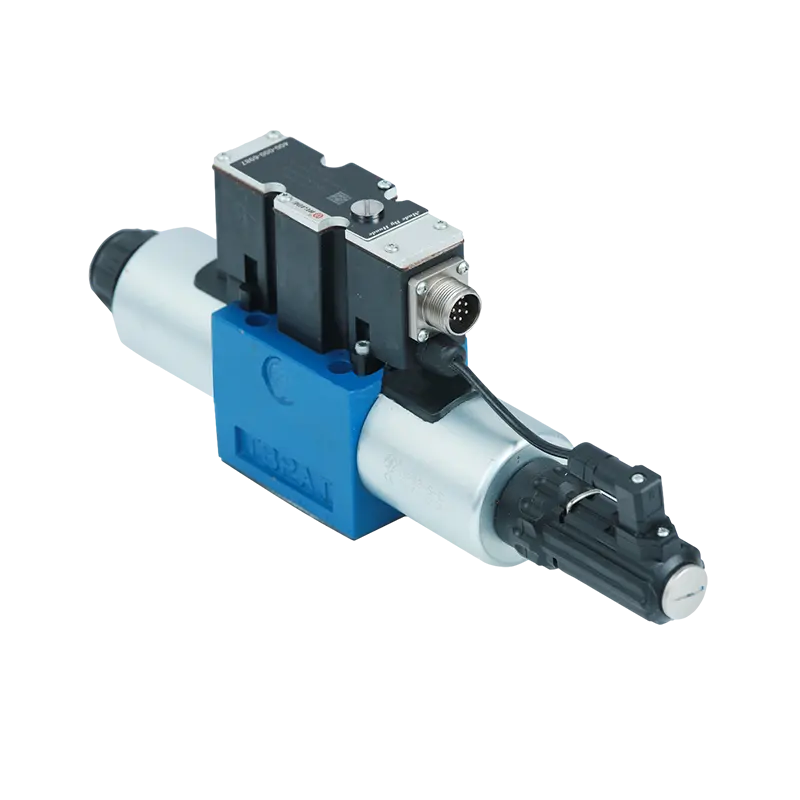
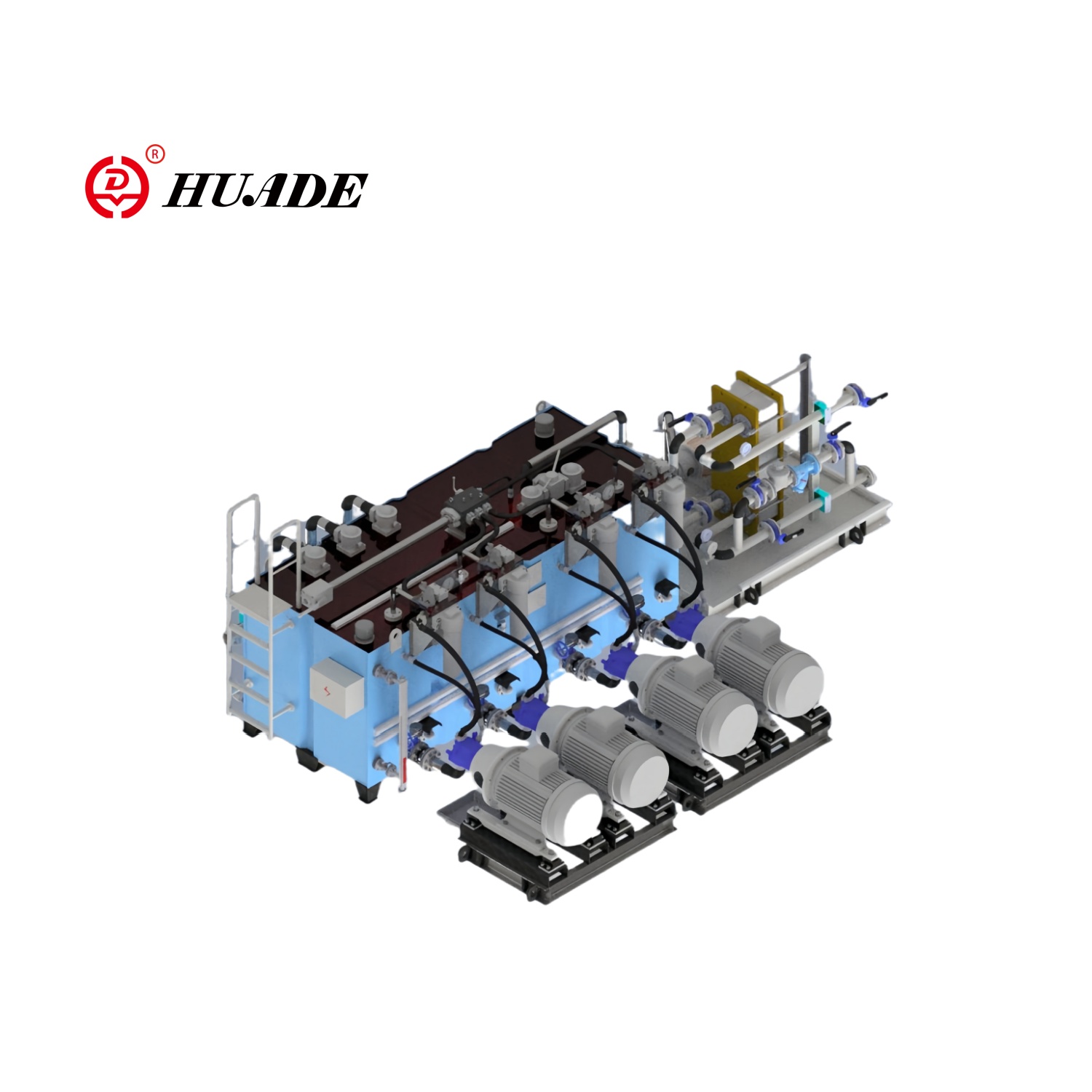
- English
- Cymraeg
- icelandic
- беларускі
- Hrvatski
- Кыргыз тили
- Maori
- Монгол хэл
- Тоҷикӣ
- O'zbek
- Lëtzebuergesch
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- فارسی
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Slovenský jazyk
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- Srpski језик